![]()
Fresh smell and colour
A pleasant, natural smell (not sour or mouldy) and a bright, natural colour
![]()
Fresh smell and colour
A pleasant, natural smell (not sour or mouldy) and a bright, natural colour
![]()
Clean and safe
Free from mould, dust, foreign objects, or harmful bacteria
![]()
Stable and palatable
Stays fresh for at least 24 hours, preventing sorting by cows
Identifying risk indicators is the first step in preventing microbial spoilage, but further assessment is needed to determine its severity. Early detection helps farmers take action before herd health and productivity are affected. Both on-farm and laboratory methods can be used to evaluate aerobic spoilage risk. Quick on-farm tests include visual and smell assessments, temperature checks, and pH measurements - simple and fast ways to monitor feed quality. For more precise analysis, laboratory testing provides detailed insights.
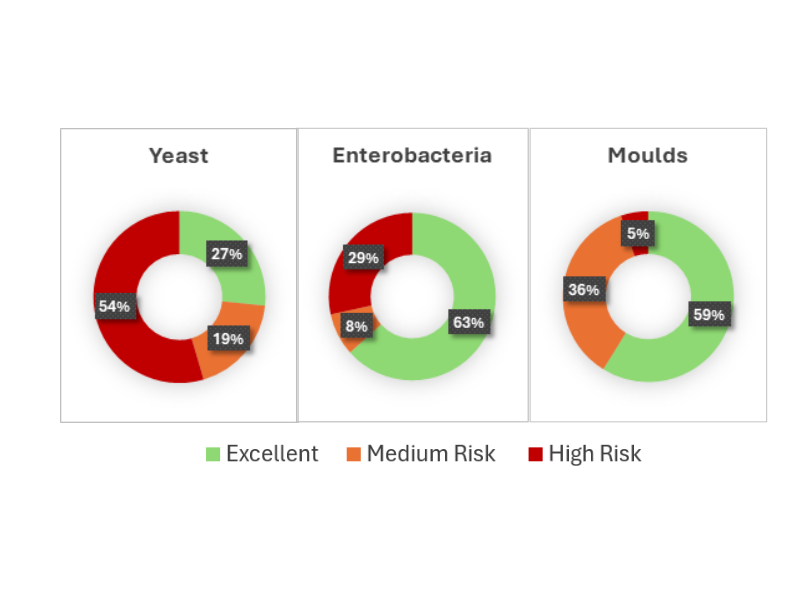
Figure 1. The figure demonstrates a representation of approximately 600 TMR and silage samples analyzed by Masterlab. The illustration demonstrates the occurrences of yeast, moulds and enterobacteria counts and the risks.
Identifying risk indicators is the first step in preventing microbial spoilage, but further assessment is needed to determine its severity.

Keep an eye out for:
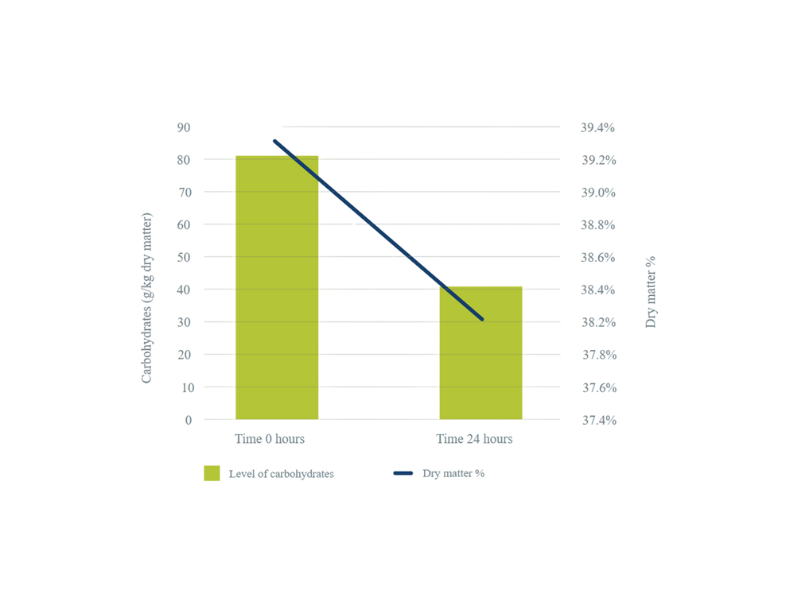
Microbial growth in the TMR leads to the breakdown of easily fermentable proteins and carbohydrates into water and CO2 lowering the nutritional value of the feed. This process reduces the dry matter content, ultimately lowering the overall nutritional value of the dairy feed.
Spoilage of TMR as a result of increased microbial growth reduces the palatability of the TMR. Cows may sort certain components of TMR if it is left in the bunk for an extended period, leading to imbalanced nutrient intake, more time spent at the feeding line and reduced herd performance.
The combined effects of nutrient loss and reduced palatability can negatively impact milk production and overall feed efficiency. When cows consume a less balanced diet due to microbial spoilage, it can lead to variations in milk yield, composition, and overall farm profitability.
Figure 2. Effect of microbial fermentation in TMR on dry matter and sugar content in TMR within 24h after production – Selko study 2010.
Given that feed costs represent a significant portion of variable costs on dairy farms, controlling microbial growth in TMR is essential for maintaining animal performance and profitability. For dairy producers who prioritize maintaining the highest quality and nutritional value of TMR under varying environmental conditions, Selko TMR offers an innovative solution.
By harnessing the power of a synergistic blend of organic acids and medium chain fatty acids, both Selko TMR Dry and Selko TMR Liquid effectively inhibits the growth of harmful micro-organisms such as yeasts, moulds, and bacteria. The inclusion of buffered organic acids ensures high efficacy against undesirable microbes while minimizing corrosivity, protecting farm equipment and infrastructure. This advanced formulation helps preserve TMR quality by:
Looking for a comprehensive guide to test methods, sampling protocols and interpretation of results? Download our latest brochure 'Simple steps to keep your TMR fresh' and discover practical tips to help you maintain feed quality and optimize results.